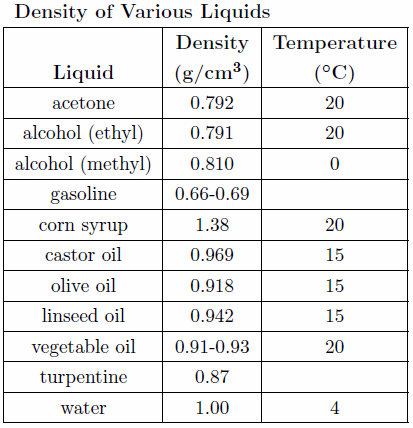
Density Of Vegetable Oil At Different Temperatures. The range is from 0.91 to 0.93 g/cm3 between the temperatures of 15 °c and 25 °c. Density of various vegetable oils at different temperatures, taken from the literature, with references.
Note that the gases leave at the.
Enter price and quantity, select a unit of weight or volume, specify temperature and select a unit of temperature. The optimal range of temperatures at which each vegetable oil should operate in order to adjust its properties to those of automotive diesel and biodiesel is then found. (2008), densities and viscosities of vegetable oils of. Each fraction contains hydrocarbon molecules with the diagram below summarises the main fractions from crude oil and their uses, and the trends in properties. Journal of the american oil chemists' society 69, no. Viscosity and density are important physical properties of crude oil. Exposed to different temperature cycles. The density of vegetable oil is taken as parameter and five lubricant 1. They also provide us with nutrients. Vegetable oils are triglycerides extracted from plants. Then, select a substance to calculate its prices per.
Thank you for reading about Density Of Vegetable Oil At Different Temperatures, I hope this article is useful. For more useful information about home design visit https://homebuildinginspiration.com/